Cassiopeia and Cepheus
Description
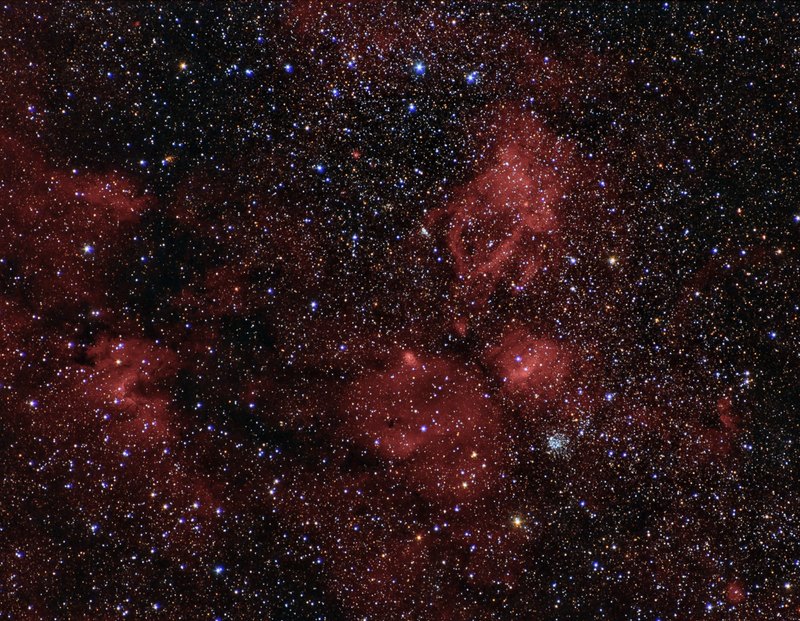
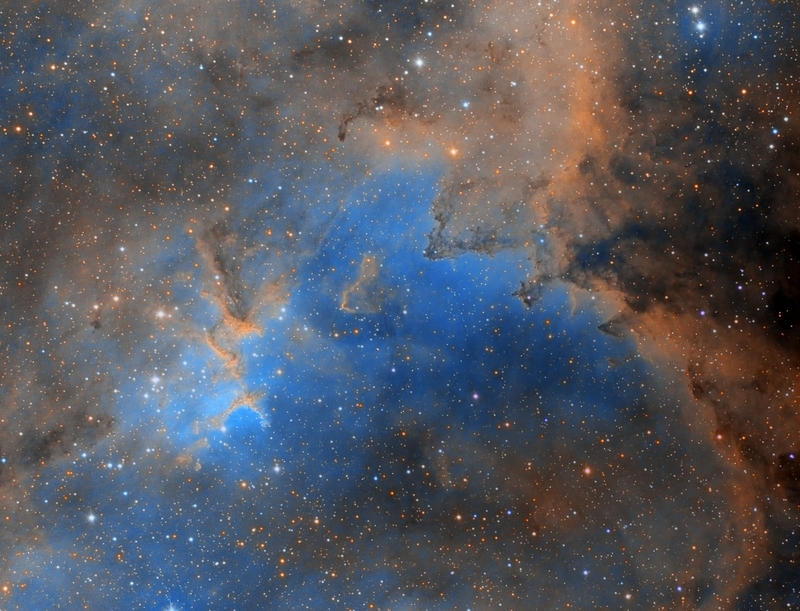
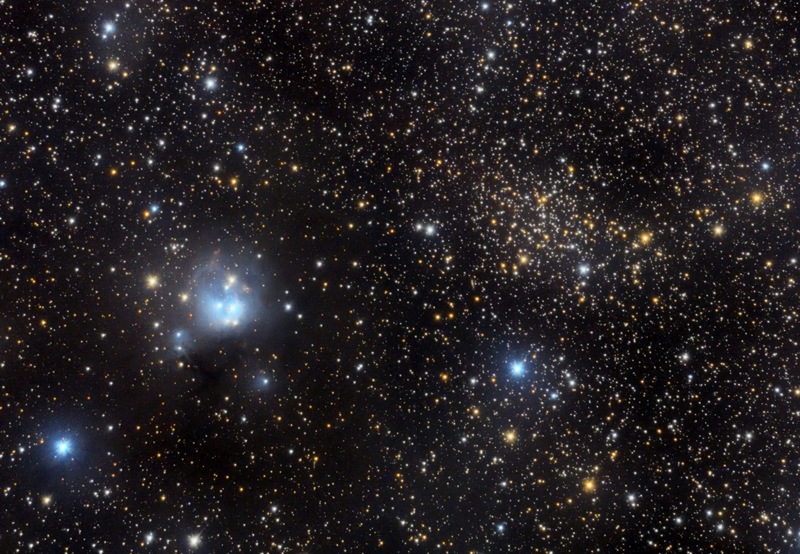
"This image shows a region between Cassioeia and Cepheus which contains multiple objects.
One the left and slightly below center located Cave Nebula, Sh2-155 or Caldwell 9, a dim and very diffuse bright nebula within a larger nebula complex containing emission, reflection, and dark nebulosity. It is located in the constellation Cepheus.
Visually it is a difficult object, but with adequate exposure, makes a striking image. The nebula gets its name Cave Nebula from the dark lane at the eastern side abutting the brightest curve of emission nebulosity which gives the appearance of a deep cave when seen through a telescope visually
In the center located NGC 7538 which is about 9,100 light-years from Earth. It is home to the biggest yet discovered protostar which is about 300 times the size of our Solar System. It is located in the Perseus Spiral Arm of the Milky Way and is probably part of the Cassiopeia OB2 complex. It is a region of active star formation including several luminous near-IR and far-IR sources
Slightly to the right of NGC 7538 located famous Bubble nebula, also known as NGC 7635, Sharpless 162, or Caldwell 11, which is a H II region emission nebula in the constellation Cassiopeia. It lies close to the direction of the open cluster Messier 52. The ""bubble"" is created by the stellar wind from a massive hot, 8.7 magnitude young central star, SAO 20575 (BD+60 2522). The nebula is near a giant molecular cloud which contains the expansion of the bubble nebula while itself being excited by the hot central star, causing it to glow. It was discovered in 1787 by William Herschel. The star SAO 20575 or BD+602522 is thought to have a mass of 10-40 Solar masses.
Below Bubble nebula located Messier 52 (also known as M 52 or NGC 7654) which is an open cluster in the Cassiopeia constellation. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1774. M52 can be seen from Earth with binoculars.
Due to interstellar absorption of light, the distance to M 52 is uncertain, with estimates ranging between 3,000 and 7,000 light years. One study identified 193 probable members of the cluster, with the brightest member being magnitude 11. Messier 52 is evaluated at about 35 million years old.
Above Bubble nebula located the Claw Nebula, also known as Sh2 -157, which is an emission nebula. It is located on the arm of Perseus and is directly connected with the largest association OB Cassiopeia OB2 . The northern part of the cloud has a ring shape, caused by the action of stellar wind of several giant stars, while the southern sector seems excited by light of the stars of spectral type O."
Equipment and processing
Telescope: 135mm F2.8 lens
Mount: Meade LXD55
Camera: ST 8300M
Filters: Baader HaRGB
Guiding: PHD
Processing: PixInsight
Capture software: Maxim
Exposures: Ha: Bin1 24x1200, RGB: Bin1 24x120
Location: Hatteras,NC